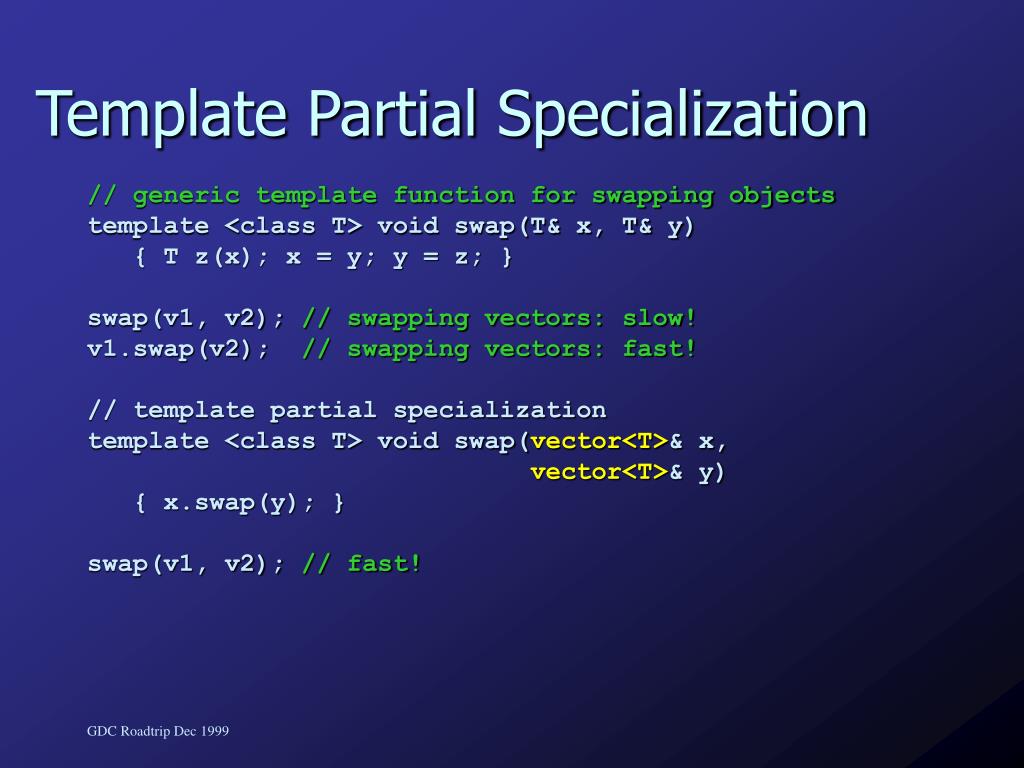
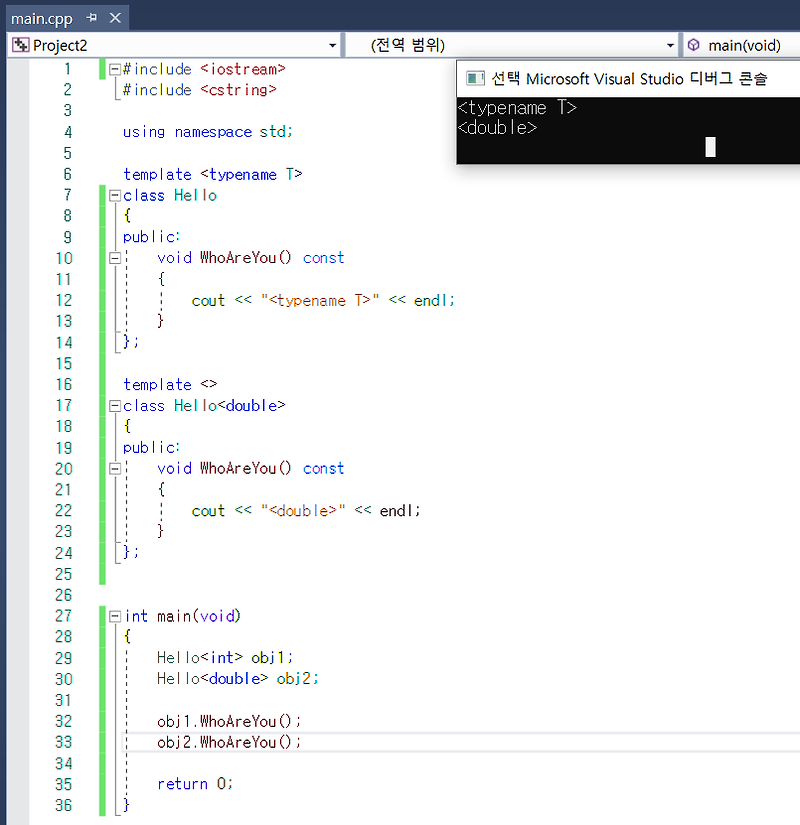
C++ Partial Template Specialization
C++ Partial Template Specialization - Web 1 this isn't a partial specialization, foo takes two parameters and you only specify one in foo::foo1. Web when myintptr is defined with an int* template parameter, the compiler sees that we have defined a partially specialized template class that works with any pointer. Template < template_parameter_list > declaration_name < template_argument_list > declaration_body. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic functions and thus provide support for generic programming. When a class or variable (since c++14)template is instantiated, and there are partial specializations available, the compiler has to decide if the primary template is going to be used or one of its partial specializations. A partial specialization has both a template argument list and a template parameter list. Web partial template specialization allows us to specialize classes (but not individual functions!) where some, but not all, of the template parameters have been. Web a partial template specialization is a class template definition in which part of the arguments of a more generic class template (primary) are defined. Web whether an explicit specialization of a function or variable (since c++14) template is inline /constexpr (since c++11) /constinit/consteval (since c++20) is. For partial specializations, those restrictions aren't in place.
C++ Partial Template Specialization
A partial specialization has both a template argument list and a template parameter list. Web partial template specialization allows us to specialize classes (but not individual functions!) where some, but not all, of the template parameters have been. Web template specialization and partial template specialization by alex allain template specialization in many cases when working with templates, you'll write one.
[Solved] C++ function template partial specialization? 9to5Answer
In this blog post, we will look at how partial template specialization is. Web whether an explicit specialization of a function or variable (since c++14) template is inline /constexpr (since c++11) /constinit/consteval (since c++20) is. Web this is called template specialization. Web c++ allows to partially specialize class templates: Web for example, let's define a template and two partial specializations:
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Web template specialization and partial template specialization by alex allain template specialization in many cases when working with templates, you'll write one generic. Web c++ allows to partially specialize class templates: Those can be put in class. Web 1 this isn't a partial specialization, foo takes two parameters and you only specify one in foo::foo1. Web one such scenario that.
C++ Partial template specialization triggering static_asserts YouTube
Web whether an explicit specialization of a function or variable (since c++14) template is inline /constexpr (since c++11) /constinit/consteval (since c++20) is. Web partial template specialization allows us to specialize classes (but not individual functions!) where some, but not all, of the template parameters have been. A partial specialization has both a template argument list and a template parameter list..
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Web partial template specialization is a particular form of class template specialization. Web well the example in 14.6.5.3/2 in the c++0x draft is a partial specialization. Yes it does, it isn't a full specialization until all parameters in the template parameter list have been specialized/specified, e.g. The declaration_name is a name of a. A partial specialization has both a template.
C++ template partial specialization Why cant I match the last type in
For partial specializations, those restrictions aren't in place. When a class or variable (since c++14)template is instantiated, and there are partial specializations available, the compiler has to decide if the primary template is going to be used or one of its partial specializations. Web partial specialization (c++ only) when you instantiate a class template, the compiler creates a definition based.
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Web a partial template specialization is a class template definition in which part of the arguments of a more generic class template (primary) are defined. Web for example, let's define a template and two partial specializations: Template allows us to define generic classes and generic functions and thus provide support for generic programming. Web partial template specialization allows us to.
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Web this is called template specialization. Informally a is more specialized than b means a accepts a subset of the types that b accepts. Web partial template specialization is a particular form of class template specialization. A template has multiple types and only some of. Yes it does, it isn't a full specialization until all parameters in the template parameter.
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Usually used in reference to the c++ programming language, it allows the programmer to. For partial specializations, those restrictions aren't in place. A partial specialization has both a template argument list and a template parameter list. Web a partial template specialization is a class template definition in which part of the arguments of a more generic class template (primary) are.
C++ Partial Template Specialization
Web partial specialization (c++ only) when you instantiate a class template, the compiler creates a definition based on the template arguments you have passed. In this blog post, we will look at how partial template specialization is. Template allows us to define generic classes and generic functions and thus provide support for generic programming. For partial specializations, those restrictions aren't.
Usually used in reference to the c++ programming language, it allows the programmer to. Web c++ allows to partially specialize class templates: Web when myintptr is defined with an int* template parameter, the compiler sees that we have defined a partially specialized template class that works with any pointer. Web partial specialization allows template code to be partially customized for specific types in situations, such as: Web partial template specialization allows us to specialize classes (but not individual functions!) where some, but not all, of the template parameters have been. Web template specialization and partial template specialization by alex allain template specialization in many cases when working with templates, you'll write one generic. The declaration_name is a name of a. In this blog post, we will look at how partial template specialization is. Web for example, let's define a template and two partial specializations: Web this is called template specialization. Web 1 this isn't a partial specialization, foo takes two parameters and you only specify one in foo::foo1. Web partial specialization (c++ only) when you instantiate a class template, the compiler creates a definition based on the template arguments you have passed. Template struct s { static void foo () { std::cout << general case\n; Those can be put in class. Web an explicit specialization only has a template argument list. Web well the example in 14.6.5.3/2 in the c++0x draft is a partial specialization. A partial specialization has both a template argument list and a template parameter list. When a class or variable (since c++14)template is instantiated, and there are partial specializations available, the compiler has to decide if the primary template is going to be used or one of its partial specializations. Yes it does, it isn't a full specialization until all parameters in the template parameter list have been specialized/specified, e.g. Web one such scenario that frequently comes into play is partial template specialization.