What Direction Is The Template Strand Read
What Direction Is The Template Strand Read - Any given sequence of dna can therefore be read in six different ways: In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. Web dna is read by dna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, meaning the new strand is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction. Web 5'→3' what is the difference between the coding strand of dna and the template strand of dna? Web answer (1 of 3): Web the coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. Web the direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. The coding strand is complimentary to the template strand and the same as. (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used as a template for rna synthesis. The 5 prime end of each of these.
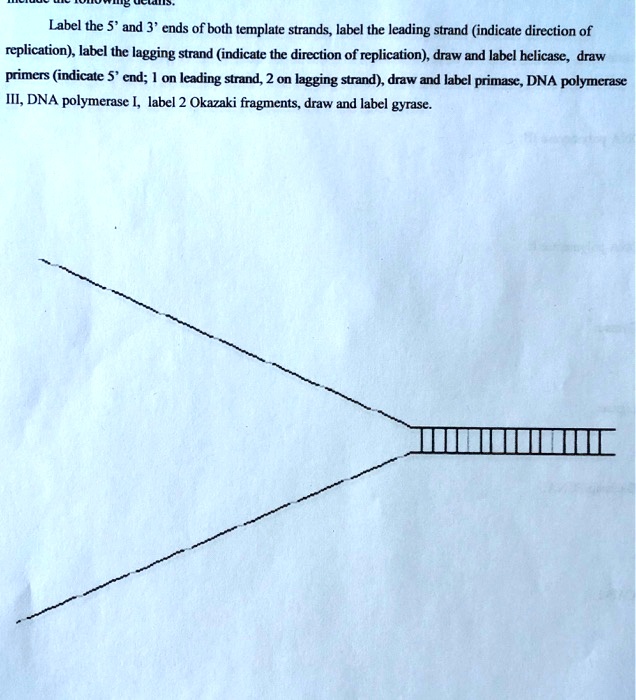
SOLVED Label the 5' and 3' ends of both template strands label the
Web answer (1 of 3): Therefore, it moves along the. 3’ to 5’ direction template strand is read in o. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). The 5 prime end.
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. Therefore, it moves along the. Web dna polymerase reads the dna template strand from the __ end of the dna molecule to the __ end. Three reading frames in one direction (starting at different nucleotides) and three in the opposite direction. The rna polymerase reads the non.
Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology
Well, that depends on the context. The 5 prime end of each of these. Three reading frames in one direction (starting at different nucleotides) and three in the opposite direction. Web answer (1 of 3): (b) find \sin 5 \pi / 6 sin5π/6.
DNA Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
(b) find \sin 5 \pi / 6 sin5π/6. 3’ to 5’ direction template strand is read in o. Genetics semiconservative replication involves a template: Web biology questions and answers. The rna polymerase reads the non.
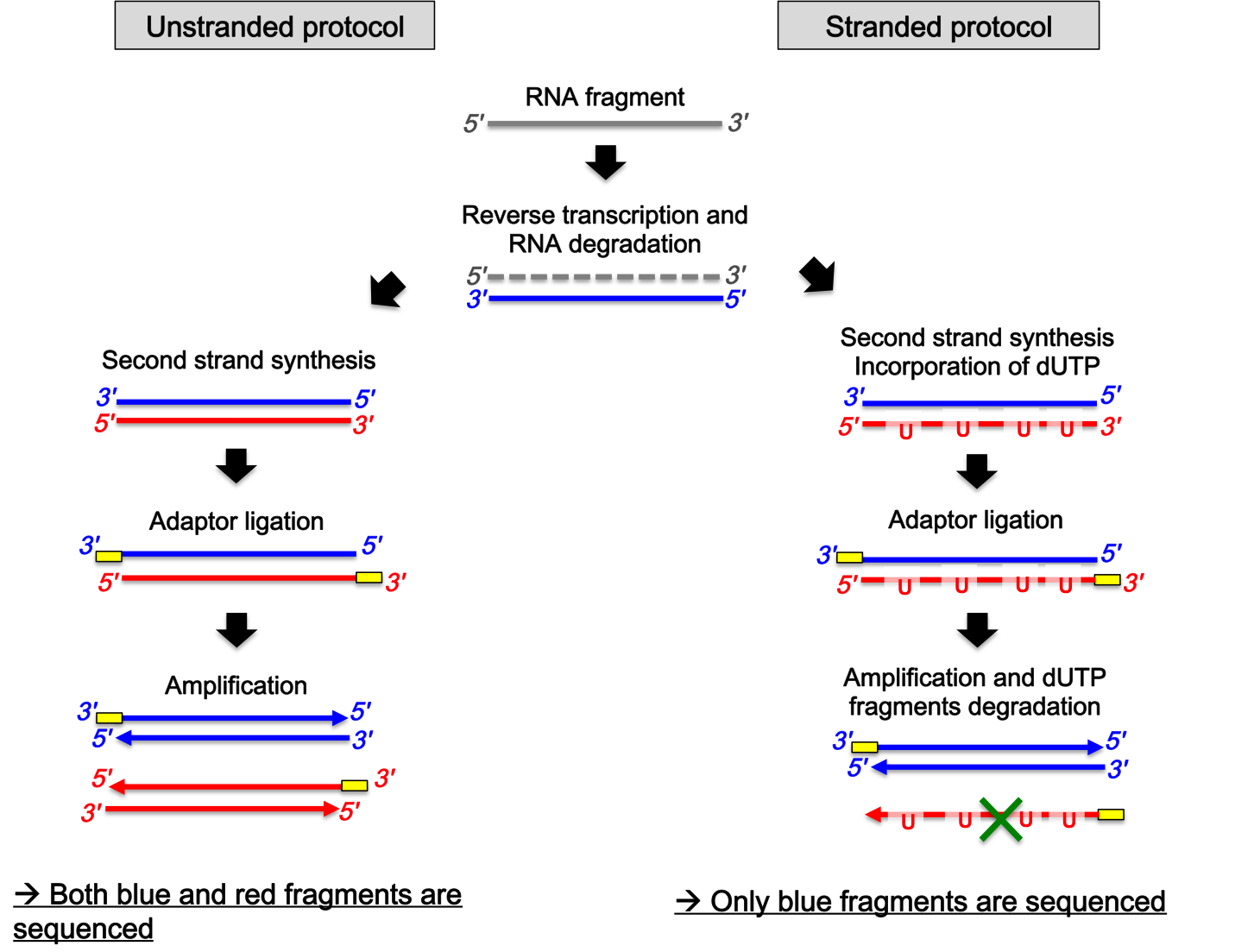
mRNAseq
Well, that depends on the context. The coding strand is complimentary to the template strand and the same as. Web answer (1 of 3): The 5 prime end of each of these. Web biology questions and answers.
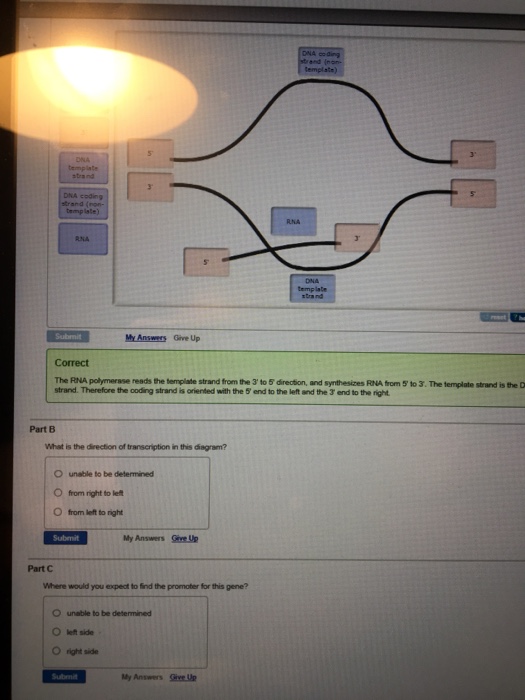
Solved What is the direction of transcription in this
Web the 5 prime end of this strand is yellow and the remainder is blue. Therefore, it moves along the. Web 5'→3' what is the difference between the coding strand of dna and the template strand of dna? Well, that depends on the context. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the dna strand.
Image result for template strand Transcription, Study biology
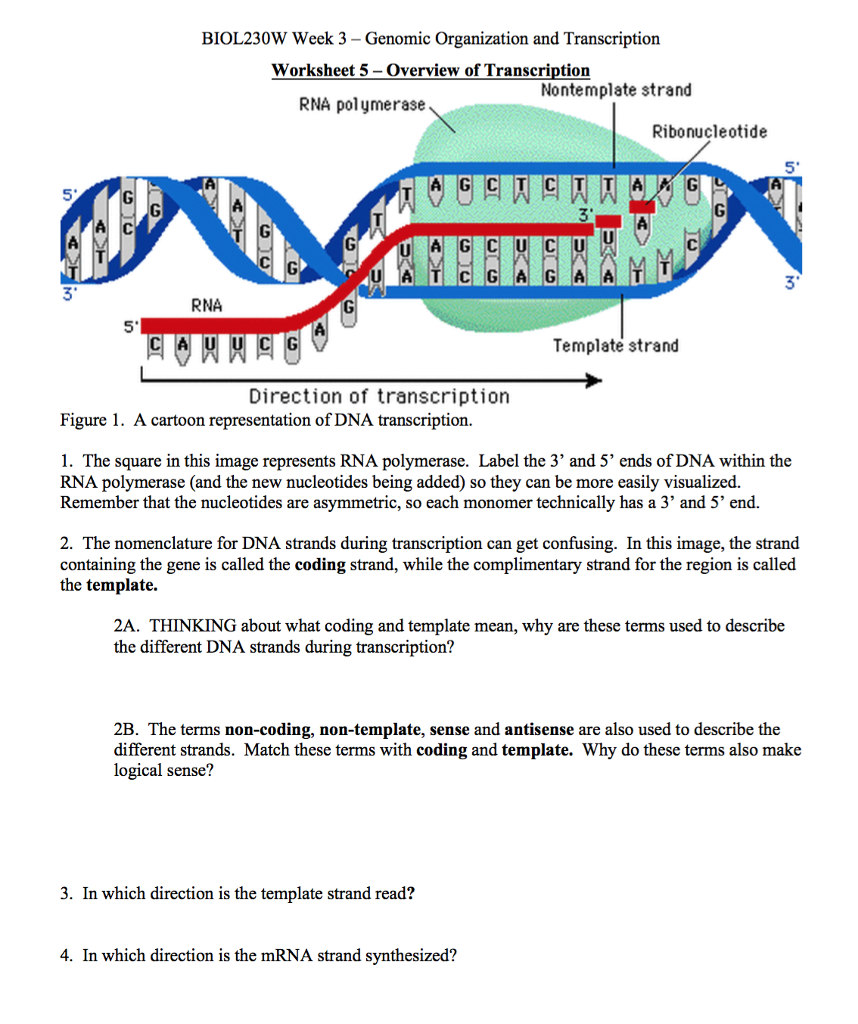
Web the direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. During transcription, the rna polymerase read the template dna strand in the 3′→5′ direction, but the mrna is formed in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Therefore, it moves along the. The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. When.
Non Template Strand
During transcription, the rna polymerase read the template dna strand in the 3′→5′ direction, but the mrna is formed in the 5′ to 3′ direction. 5’ to 3’ direction mrna is synthesized in e. Web the 5 prime end of this strand is yellow and the remainder is blue. (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used.
Non Template Strand
Web the template strand is read in the 3' to 5' direction because dna polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna chain. Web 5'→3' what is the difference between the coding strand of dna and the template strand of dna? Web the template strand is read in the 3′ to 5′ direction, which means.
Protein Synthesis Anatomy and Physiology I
The coding strand is complimentary to the template strand and the same as. Genetics semiconservative replication involves a template: During transcription, in which direction is the template strand read?c. Web biology questions and answers. Web the template strand is read in the 3' to 5' direction because dna polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing.
During transcription, the rna polymerase read the template dna strand in the 3′→5′ direction, but the mrna is formed in the 5′ to 3′ direction. The bottom black strand runs 5 prime to 3 prime and is attached to the lagging strand, which consists of a pair of okazaki fragments that run in the opposite direction. Web the direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web the template strand is read in the 3' to 5' direction because dna polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna chain. Web 5'→3' what is the difference between the coding strand of dna and the template strand of dna? The template strand is the complimentary copy of the mrna in its nucleotide base pair sequence. In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. 5’ to 3’ direction mrna is synthesized in e. Therefore, it moves along the. (b) find \sin 5 \pi / 6 sin5π/6. Web dna is read by dna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, meaning the new strand is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). Since the leading and lagging strand templates are. Web the template strand is always read in the 3’ → 5’ direction. The coding strand is complimentary to the template strand and the same as. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 3’ to 5’ direction template strand is read in o. In order for dna polymerase to do this, it must read the template strand from 3′. Any given sequence of dna can therefore be read in six different ways: